Battery Operated Thermostat Vs Hardwired: Which Saves More Money?
Choosing between a battery operated thermostat vs hardwired system isn’t just about installation convenience—it’s about long-term savings and reliability. While battery-powered thermostats offer flexible placement options and easy installation, hardwired systems provide consistent power with battery backup for added security.
In fact, smart thermostats are designed to optimize your home’s energy usage, potentially reducing utility bills over time. However, battery-powered models require yearly replacements and might offer fewer features than their hardwired counterparts. With digital thermostats serving as the brain of your HVAC system, making the right choice is crucial for maintaining comfortable temperatures and managing energy costs effectively.
We’ll help you understand which option could save you more money while meeting your specific needs, covering everything from installation costs to long-term maintenance requirements.
Understanding Battery Operated vs Hardwired Thermostats
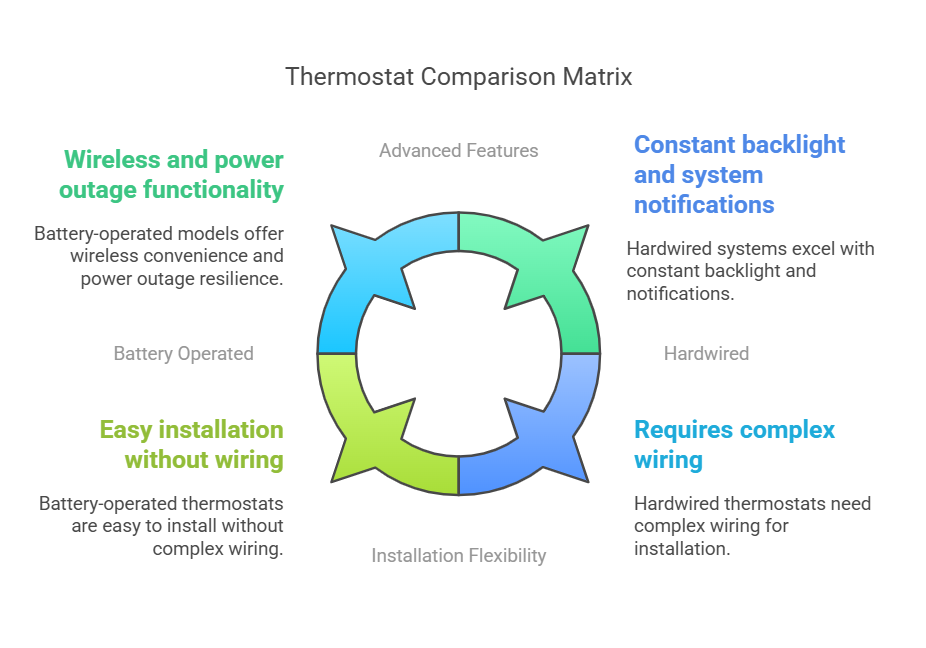
Battery operated and hardwired thermostats differ fundamentally in their power supply mechanisms and operational capabilities. Understanding these differences helps make an informed choice for your heating and cooling needs.
How Battery Operated Thermostats Work
Battery operated thermostats run on standard batteries, typically AAA size. These devices maintain programmed settings and control heating and cooling cycles through battery power alone. One significant advantage lies in their wireless nature, allowing placement anywhere without worrying about power source proximity. Additionally, battery-powered thermostats continue functioning during power outages, maintaining temperature control when needed most.
How Hardwired Thermostats Function
Hardwired thermostats operate through a low-voltage system, drawing power directly from your HVAC setup. These units utilize 24 volts of electricity through a step-down transformer that reduces the incoming 120V line voltage. The system requires specific wiring configurations, including:
- A common wire (C-wire) for continuous power supply
- Red wire (R) serving as the power source
- White wire (W) for heating control
- Yellow wire (Y) connecting to the AC compressor
Key Differences in Power Supply
The primary distinction between these systems extends beyond their power sources. Hardwired thermostats maintain constant backlight illumination and provide immediate notification of system issues through blank screens when problems arise. Furthermore, hardwired systems offer enhanced features:
- Continuous power supply without battery replacement needs
- More reliable system monitoring capabilities
- Constant backlight functionality
Battery operated models, alternatively, require periodic battery changes, ranging from several months to a couple of years depending on usage patterns. Nevertheless, they excel in installation flexibility and don’t need complex wiring setups.
Both types serve specific needs effectively, yet their power supply differences significantly impact long-term maintenance requirements and functionality. Notably, hardwired systems often provide more advanced features and customization options compared to their battery-powered counterparts.
Initial Costs and Installation Comparison
The financial investment in a new thermostat extends beyond the initial purchase price, encompassing both equipment and installation costs. A thorough understanding of these expenses helps in making an informed decision.
Battery Operated Thermostat Purchase and Setup Costs
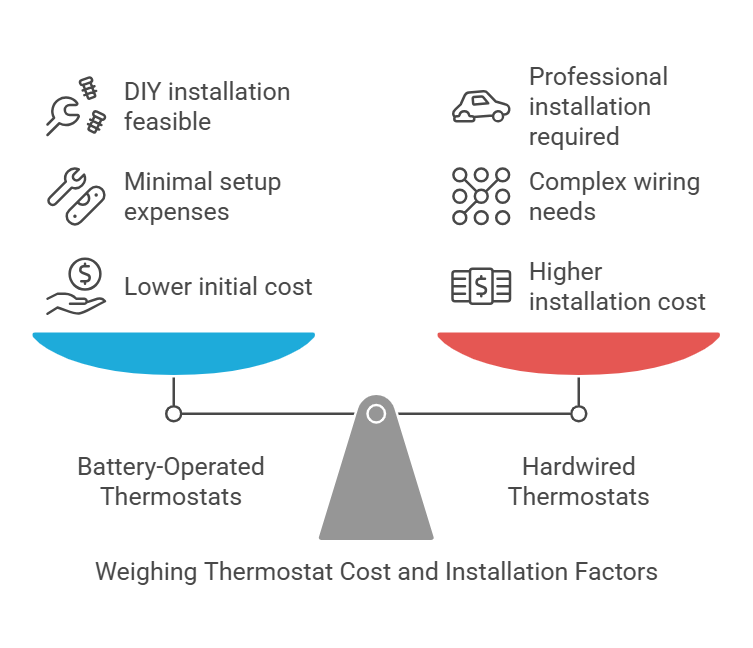
Basic battery-operated thermostats start at USD 15.00 for simple mechanical units. More advanced battery-powered models with WiFi capabilities range from USD 70.00 to USD 200.00. Generally, these units require minimal setup costs since they don’t need complex wiring modifications.
Hardwired Thermostat Installation Expenses
Professional installation of hardwired thermostats involves more substantial costs. The total expense typically ranges from USD 140.00 to USD 350.00, which includes both the unit and professional installation. Specifically, labor costs average between USD 80.00 to USD 200.00.
For hardwired systems requiring new C-wire installation, expect additional charges of USD 90.00 to USD 135.00. Moving a thermostat location costs between USD 135.00 to USD 450.00, depending on the complexity of rewiring and wall repairs.
DIY vs Professional Installation Requirements
Professional installation primarily offers several advantages:
- Licensed electricians typically complete installations in under two hours at USD 65.00 to USD 100.00 per hour
- Professionals ensure proper wiring compatibility and system functionality
- Installation warranties protect against future issues
Alternatively, DIY installation remains possible for those with basic electrical knowledge. Yet, incorrect installation can lead to:
- Electrical circuit shorts
- Damage to new thermostats
- Potential warranty violations
- HVAC system malfunctions
Ultimately, the decision between DIY and professional installation depends on system complexity and personal expertise. Professional installation becomes particularly important for smart thermostats or systems with unusual configurations like multizone baffles or dual-fuel systems.
Long-Term Operating Costs
Regular maintenance costs shape the long-term financial picture of thermostat ownership. Understanding these ongoing expenses helps homeowners make informed decisions about their heating and cooling control systems.
Battery Replacement Frequency and Expenses
Battery-powered thermostats require consistent attention to power supply. Most homeowners replace batteries once annually, though some systems need bi-annual changes. High-quality batteries typically last between three months to five years, depending on usage patterns and environmental conditions.
Several factors contribute to accelerated battery drain:
- Corroded contacts affecting power transmission
- Aging internal components drawing excess power
- Incorrect battery voltage installation
Energy Consumption Analysis
Hardwired thermostats demonstrate superior reliability in power consumption patterns. Alternatively, battery-operated models might experience performance fluctuations as batteries deplete. Consequently, this affects the system’s ability to maintain precise temperature control and programming accuracy.
Modern smart thermostats, primarily hardwired models, receive power directly from HVAC systems. This setup ensures consistent performance without the variability associated with battery power levels. Moreover, many contemporary units include rechargeable batteries that draw power from the HVAC transformer, combining reliability with backup security.
Maintenance Requirements and Costs
Both types require different maintenance approaches. Battery-operated thermostats need regular battery changes, essentially creating a predictable maintenance schedule. For hardwired systems with backup batteries, annual replacement ensures continuous operation during power outages.
Proper maintenance extends beyond simple battery replacement. Regular cleaning of battery contacts prevents corrosion, which could otherwise lead to system failures. Additionally, older thermostats often consume more power, potentially requiring more frequent maintenance.
For optimal performance, setting a fixed annual date for battery replacement helps prevent unexpected system failures. This practice, combined with bi-annual HVAC service appointments, ensures reliable temperature control throughout the year. Primarily, using recognized battery brands provides consistent power for at least twelve months, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated costs.
Reliability and Performance Factors
Performance reliability stands as a crucial factor in distinguishing between battery operated and hardwired thermostats. Each type exhibits distinct characteristics under various operating conditions.
Power Outage Performance
Battery operated thermostats maintain basic functionality during power outages, primarily operating as traditional thermostats rather than smart devices. Alternatively, hardwired systems with battery backup provide temporary operation, typically lasting a couple of hours before complete shutdown. Subsequently, these systems require approximately one hour to restore full functionality once power returns.
Programming and Settings Retention
Programming retention varies significantly between thermostat types. Hardwired systems face potential programming loss due to:
- Power surges affecting internal components
- Software glitches disrupting stored settings
- Circuit breaker interruptions
Battery operated thermostats retain programming as long as battery power remains sufficient. Accordingly, when batteries deplete, these units revert to default factory settings, necessitating reprogramming.
System Response Time and Accuracy
Response time, measured by a 63.2% step change in temperature, determines how quickly thermostats react to environmental changes. Digital thermostats demonstrate superior accuracy compared to mechanical alternatives. Several factors influence response time accuracy:
- Internal construction design
- Environmental conditions
- Sensor size specifications
Digital electronic thermostats excel in maintaining consistent temperature measurements. The accuracy remains stable through a temperature sensor’s response curve, ensuring reliable performance across varying conditions. Primarily, these units minimize temperature overshooting through built-in anticipators that adjust system timing before reaching setpoints.
For optimal performance, hardwired thermostats utilize PID loops and high-accuracy sensors in situations demanding precise control. These components enable faster response times and more accurate temperature readings compared to basic battery operated models. The thermal mass of both types affects measurement lag, though digital systems compensate through advanced algorithms.
Smart Features and Integration
Modern thermostats blend advanced technology with user convenience, offering features that extend far beyond basic temperature control. Both battery operated and hardwired models now incorporate smart capabilities, albeit with distinct differences in functionality.
WiFi Connectivity Options
WiFi-enabled thermostats provide enhanced control over indoor temperatures. Primarily, hardwired models offer more reliable WiFi connections because of their constant power supply. Battery operated WiFi thermostats, alternatively, must balance connectivity with power conservation to extend battery life.
These devices connect through built-in WiFi radios, enabling network integration and internet connectivity. Indeed, many models save programming settings without batteries, requiring only time resets after power interruptions.
Smart Home Compatibility
Smart thermostats seamlessly integrate with various home automation platforms. The most popular integration options include:
- Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant for voice commands
- Apple HomeKit for iOS users
- Samsung SmartThings for comprehensive home control
- IFTTT for custom automation scenarios
Alongside voice control capabilities, these systems support advanced features like geofencing and automated scheduling. Smart thermostats can trigger other compatible devices, creating a coordinated home environment.
Remote Control Capabilities
Remote management stands out as a defining feature of modern thermostats. Through dedicated mobile apps, users can:
- Monitor HVAC system performance
- Receive smart alerts and maintenance reminders
- Adjust temperature settings from anywhere
- Create custom scheduling profiles
The Net/X WiFi thermostat series demonstrates these capabilities with features like dual login security and equipment efficiency monitoring. Similarly, many models include remote sensor compatibility, allowing temperature monitoring in multiple rooms.
Ultimately, smart features contribute to energy savings through intelligent scheduling and remote adjustments. These capabilities enable users to optimize comfort while maintaining efficient operation, with some models offering utility savings programs and rewards for upgrading to smart thermostats.
Comparison
| Feature | Battery Operated Thermostat | Hardwired Thermostat |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | $15 (basic) to $200 (WiFi-enabled) | Unit + Installation: $140-$350 |
| Installation Cost | Minimal (DIY friendly) | $80-$200 labor costs + Additional $90-$135 for C-wire installation |
| Power Source | AAA batteries | 24V from HVAC system |
| Battery Replacement | Annual to bi-annual replacement needed | Only needed for backup power |
| Power Outage Function | Maintains full functionality | Requires battery backup, operates for few hours |
| Placement Flexibility | High – can be placed anywhere | Limited by wiring requirements |
| Wiring Requirements | None | C-wire and specific wiring configuration needed |
| Programming Retention | Retains while batteries have power | May lose settings during power surges |
| Display Features | Limited backlight to conserve power | Constant backlight illumination |
| WiFi Reliability | Limited by battery conservation | More reliable due to constant power |
| Maintenance Needs | Regular battery changes and contact cleaning | Minimal maintenance required |
| Long-term Reliability | Dependent on battery condition | More reliable with consistent power supply |
Conclusion
Choosing between battery-operated and hardwired thermostats requires careful consideration of several key factors. Battery-operated models shine through their flexible placement options and lower initial costs, starting at $15 for basic units. These systems prove particularly valuable during power outages, maintaining full functionality when other home systems fail.
Hardwired thermostats, though requiring professional installation ranging from $140 to $350, offer superior long-term reliability and advanced features. Their constant power supply enables better WiFi connectivity and smart home integration, while minimizing ongoing maintenance needs.